Motivation
"Artificial Intelligence (AI) is considered a major innovation that could disrupt many things. Some people even compare it to the Internet. A large investor firm predicted that some AI startups could become the next Apple, Google or Amazon within five years"- Prof. John Vu, Carnegie Mellon University.
Using chatbots to support our daily tasks is super useful and interesting. In fact, "Jenkins CI, Jira Cloud, and Bitbucket" have been becoming must-have apps in Slack of my team these days.
There are some existing approaches for chatbots including pattern matching, algorithms, and neutral networks. RiveScript is a scripting language using "pattern matching" as a simple and powerful approach for building up a Chabot.
Architecture
Actually, it was flexible to choose a programming language for the used Rivescript interpreter like Java, Go, Javascript, Python, and Perl. I went with Java.Used Technologies and Tools
- Oracle JDK 1.8.0_151
- Apache Maven 3.5.2
- Apache Tomcat 7.0.85
- RiveScript-Java
- Jersey sever/client
- MyFaces
Module ChatBot Backend
I had a backend for chatbot's brain which provided APIs responding to received messages from users via a GUI.1. Generate a web app project via Maven
mvn archetype:generate \ -DgroupId=vn.nvanhuong \ -DartifactId=chatbot_rivescript_backend \ -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-webapp \ -DinteractiveMode=false;
Tips: When importing the project into Eclipse, I encountered an error "The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path". I solved it by "Right click on the project/Properties/Project Facets/Runtimes/Check Apache Tomcat v.7.0"
2. Add dependencies needed in `pom.xml`
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>vn.nvanhuong</groupId> <artifactId>chatbot_rivescript_backend</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>chatbot_rivescript_backend Maven Webapp</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <dependencies> <!-- ChatBot Brain --> <dependency> <groupId>com.rivescript</groupId> <artifactId>rivescript-core</artifactId> <version>0.10.0</version> </dependency> <!-- RESTful APIs --> <dependency> <groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId> <artifactId>jersey-server</artifactId> <version>1.8</version> </dependency> <!-- JSON --> <dependency> <groupId>org.json</groupId> <artifactId>json</artifactId> <version>20160810</version> </dependency> <!-- Unit tests --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>chatbot_rivescript_backend</finalName> </build> </project>
3. Create chatbot's brain with RiveScript
I created a file "chatbot_brain.rive" under the folder "src/main/resources/rivescript". I copied the content of template file "rs_standard.rive" at https://www.rivescript.com/try+ hello bot - Hello human!
4. Create RESTful APIs
package vn.nvanhuong.chatbot.rivescript.backend;
import javax.ws.rs.POST;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import com.rivescript.Config;
import com.rivescript.RiveScript;
import com.sun.jersey.spi.resource.Singleton;
@Path("/bot")
@Singleton
public class ChatBot {
private RiveScript bot;
public ChatBot() {
String rivescriptFilePath = ChatBot.class.getClassLoader().getResource("rivescript").getFile();
bot = new RiveScript(Config.utf8());
bot.loadDirectory(rivescriptFilePath);
bot.sortReplies();
}
@POST
public String getMsg(String msg) {
return bot.reply("user", msg);
}
}
5. Configure RESTful at `web.xml`
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<display-name>Restful Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>jersey-serlvet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
com.sun.jersey.spi.container.servlet.ServletContainer
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>com.sun.jersey.config.property.packages</param-name>
<param-value>vn.nvanhuong.chatbot.rivescript.backend</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>jersey-serlvet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/rest/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
6. Write a test case
package vn.nvanhuong.chatbot.rivescript.backend.test;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.junit.Test;
import vn.nvanhuong.chatbot.rivescript.backend.ChatBot;
public class ChatBotTest {
@Test
public void should_say_hello() {
ChatBot bot = new ChatBot();
assertEquals("Hello Human!", bot.getMsg("Hello Bot"));
}
}
7. Test the API with Postman
URL: http://localhost:8080/chatbot_rivescript_backend/rest/botModule ChatBot GUI
1. Generate a web app project via Maven
mvn archetype:generate \ -DgroupId=vn.nvanhuong \ -DartifactId=chatbot_rivescript_gui \ -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-webapp \ -DinteractiveMode=false
2. Add dependencies needed in pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>vn.nvanhuong</groupId> <artifactId>chatbot_rivescript_gui</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>chatbot_rivescript_gui Maven Webapp</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <dependencies> <!-- JAX-RS Client --> <dependency> <groupId>org.glassfish.jersey.core</groupId> <artifactId>jersey-client</artifactId> <version>2.25.1</version> </dependency> <!-- JSF Pages --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.myfaces.core</groupId> <artifactId>myfaces-api</artifactId> <version>2.2.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.myfaces.core</groupId> <artifactId>myfaces-impl</artifactId> <version>2.2.0</version> </dependency> <!-- Unit test --> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>chatbot_rivescript_gui</finalName> </build> </project>
3. Configure JSF at web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
version="2.5">
<!-- JSF mapping -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>javax.faces.webapp.FacesServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.xhtml</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- welcome page -->
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.xhtml</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
4. Create a GUI
Rename index.jsp to index.xthml
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:p="http://xmlns.jcp.org/jsf/passthrough">
<h:head>
<title>RiveScript</title>
<style>
.container {
display: block;
margin: 50px auto;
width: 90%;
}
.chatbox {
height: 600px;
border: solid 1px #039;
background-image: url(bot_logo.png);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: center;
background-size: contain;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.chatbox .bot-dialog {
width: 90%;
border: dashed 1px purple;
text-align: center;
background-color: orange;
}
.chatbox .bot-dialog > span{
font-size: larger;
}
.message {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.message > input.message-input {
width: 90%;
margin-top: 10px;
line-height: 2.3;
}
.message > input.submit {
width: 9%;
background-color: #039;
color: white;
font-size: 15px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.message-display > span {
font-style: italic;
}
.message-display > label {
font-weight: bold;
}
.message-display {
margin-top: 5px;
}
</style>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<h:form>
<h:panelGroup layout="block" styleClass="container">
<h:panelGroup layout="block" styleClass="chatbox">
<h:panelGroup layout="block" styleClass="bot-dialog">
<h:outputText id="botMessage" value="#{controller.botMessage}" escape="false"/>
</h:panelGroup>
</h:panelGroup>
<h:panelGroup layout="block" styleClass="message">
<h:inputText id="input" value="#{controller.humanMessage}" styleClass="message-input"
p:placeholder="Send a message to the bot"
p:autofocus="true"
onblur="this.focus()"/>
<h:commandButton id="button" value="Send" actionListener="#{controller.onSend}" styleClass="submit"/>
</h:panelGroup>
<h:panelGroup layout="block" styleClass="message-display" rendered="#{not empty controller.humanMessageDisplay}">
<h:outputLabel for="messageDisplay" value="You just said: "/>
<h:outputText id="messageDisplay" value="#{controller.humanMessageDisplay}"/>
</h:panelGroup>
</h:panelGroup>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
5. Create a Controller to call the RESTful APIs
package vn.vanhuong.chatbot.rivescript.gui;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.event.ActionEvent;
import javax.ws.rs.client.ClientBuilder;
import javax.ws.rs.client.Entity;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@ManagedBean(name = "controller")
public class Controller {
private String humanMessage;
private String botMessage;
private String humanMessageDisplay;
public void onSend(ActionEvent event) {
Response response = ClientBuilder.newClient().target("http://localhost:8080/chatbot_rivescript_backend/rest/bot")
.request(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED)
.post(Entity.entity(humanMessage, MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED));
this.botMessage = response.readEntity(String.class);
this.humanMessageDisplay = humanMessage;
this.humanMessage = null;
}
public String getHumanMessage() {
return humanMessage;
}
public void setHumanMessage(String humanMessage) {
this.humanMessage = humanMessage;
}
public String getBotMessage() {
return botMessage;
}
public void setBotMessage(String botMessage) {
this.botMessage = botMessage;
}
public String getHumanMessageDisplay() {
return humanMessageDisplay;
}
public void setHumanMessageDisplay(String humanMessageDisplay) {
this.humanMessageDisplay = humanMessageDisplay;
}
}
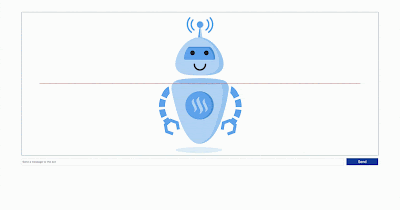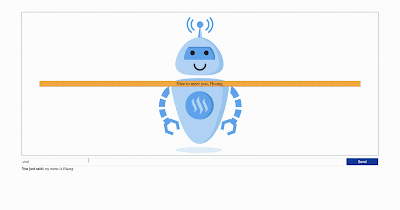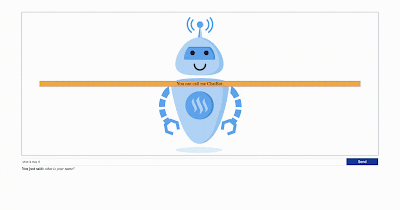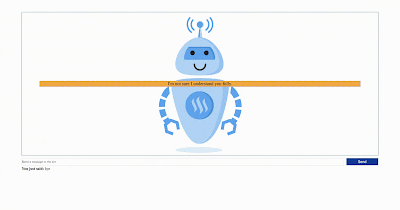
6. Enjoy playing with your ChatBot
Check out my source code as below
- Backend: https://github.com/vnnvanhuong/chatbot_rivescript_backend.git- GUI: https://github.com/vnnvanhuong/chatbot_rivescript_gui.git
References:
[1]. http://science-technology.vn/?p=5761
[2]. https://www.rivescript.com/interpreters
[3]. https://github.com/aichaos/rivescript-java
[4]. https://youtu.be/wf8w1BJb9Xc


Comments
Post a Comment